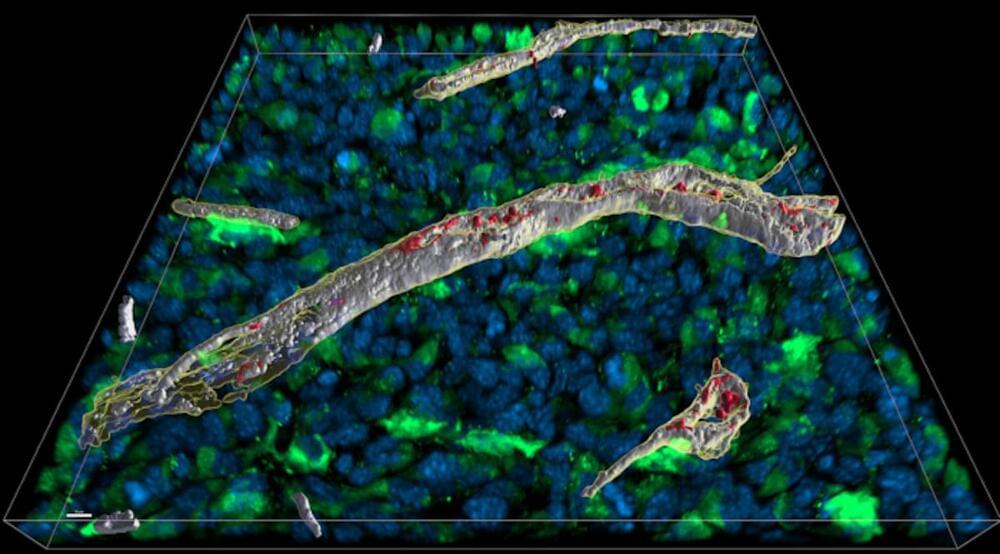
The immune system can mount crucial defenses when our bodies are threatened by pathogens. But those defenses have to be carefully contained. When processes in the human system go awry, serious diseases can result. Now scientists have learn more about how connective tissue works to control inflammatory molecules so they can act locally but don’t spread throughout the body. The findings have been reported in Nature Immunology.
Cytokines are immune signaling molecules, and they help T cells communicate. Interferon-gamma is one cytokine that plays a critical role in the elimination of bacterial and viral invaders. Scientists have discoverd that this molecule uses a sequence of four amino acids to bind to the extracellular matrix that connects cells and mediates interactions between them. Interferon-gamma gets caught in that connective tissue, and cannot spread to other areas.









Leave a reply