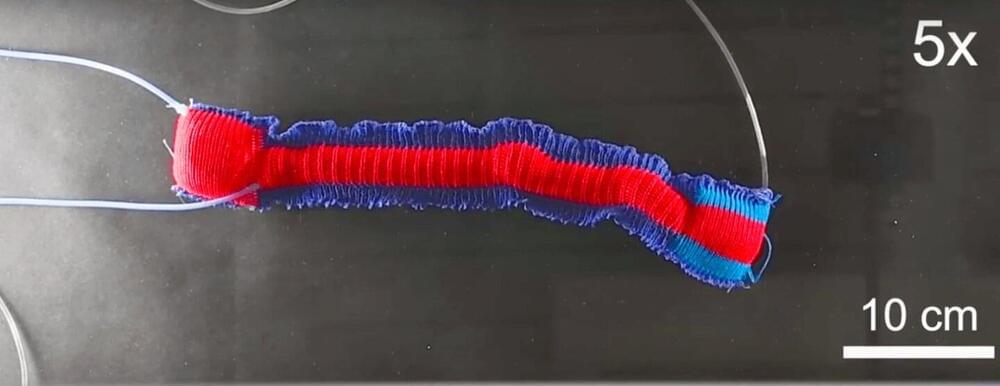
Soft robotics have several key advantages over rigid counterparts, including their inherent safety features—soft materials with motions powered by inflating and deflating air chambers can safely be used in fragile environments or in proximity with humans—as well as their flexibility that enables them to fit into tight spaces. Textiles have become a choice material for constructing many types of soft robots, especially wearables, but the traditional “cut and sew” methods of manufacturing have left much to be desired.
Now, researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have established a new approach for additively manufacturing soft robotics, using a 3D knitting method that can holistically “print” entire soft robots. Their work is reported in Advanced Functional Materials.
“The soft robotics community is still in the phase of seeking alternative materials approaches that will enable us to go beyond more classical rigid robot shapes and functions,” says Robert Wood, senior corresponding author on the paper, who is the Harry Lewis and Marlyn McGrath Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences at SEAS.









Leave a reply